Hometown Animal Hospital

Canine Oral Swellings
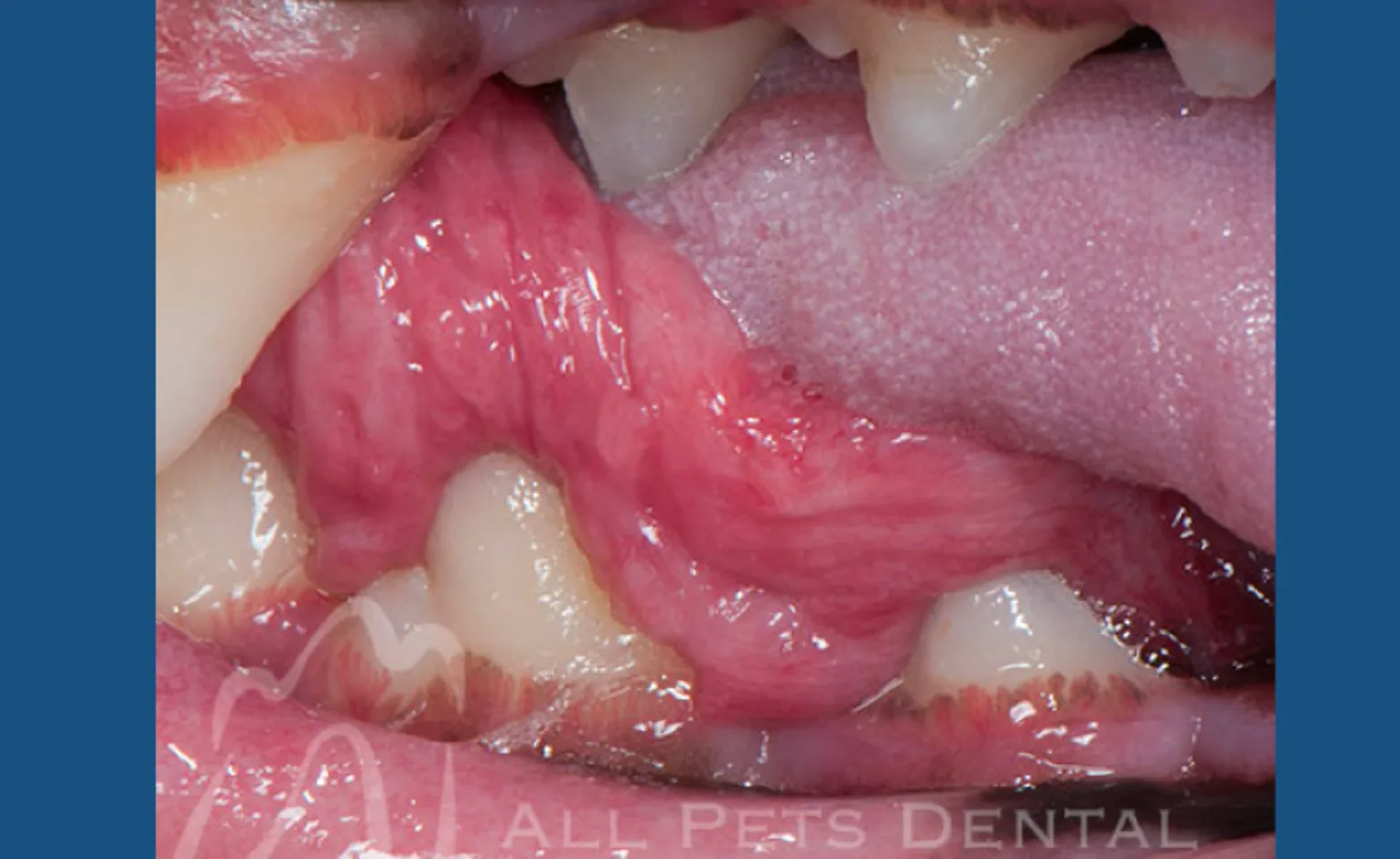
Gum chewers Lesion
Named gum chewers lesion because affected dogs appear to be chewing gum. Visibly there will be growths under the back part of the tongue. Treatment involves laser removal of the excessive tissue.
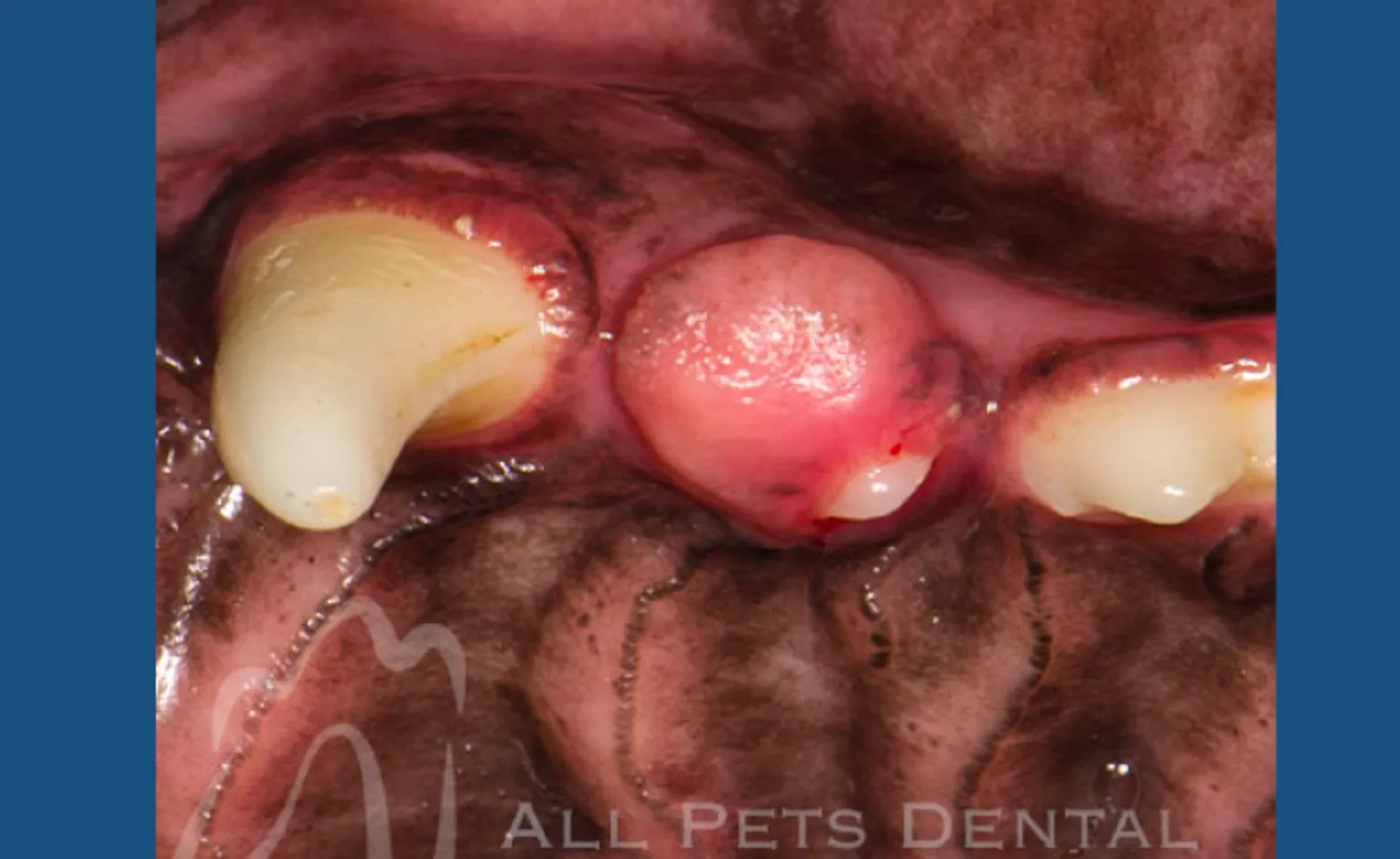
Peripheral Odontogentic Fibroma (POF)
Peripheral odontogenic fibromas include fibromatous and ossifying epulides. Epulis (plural=epulides) is a general term referring to a gingival mass of any type. The ossifying type is distinguished from the fibromatous type by containing varying amounts of bone, osteoid, dentinoid, or cementum-like tissue. Peripheral odontogenic fibromas are considered benign. Complete surgical removal is the treatment of choice.
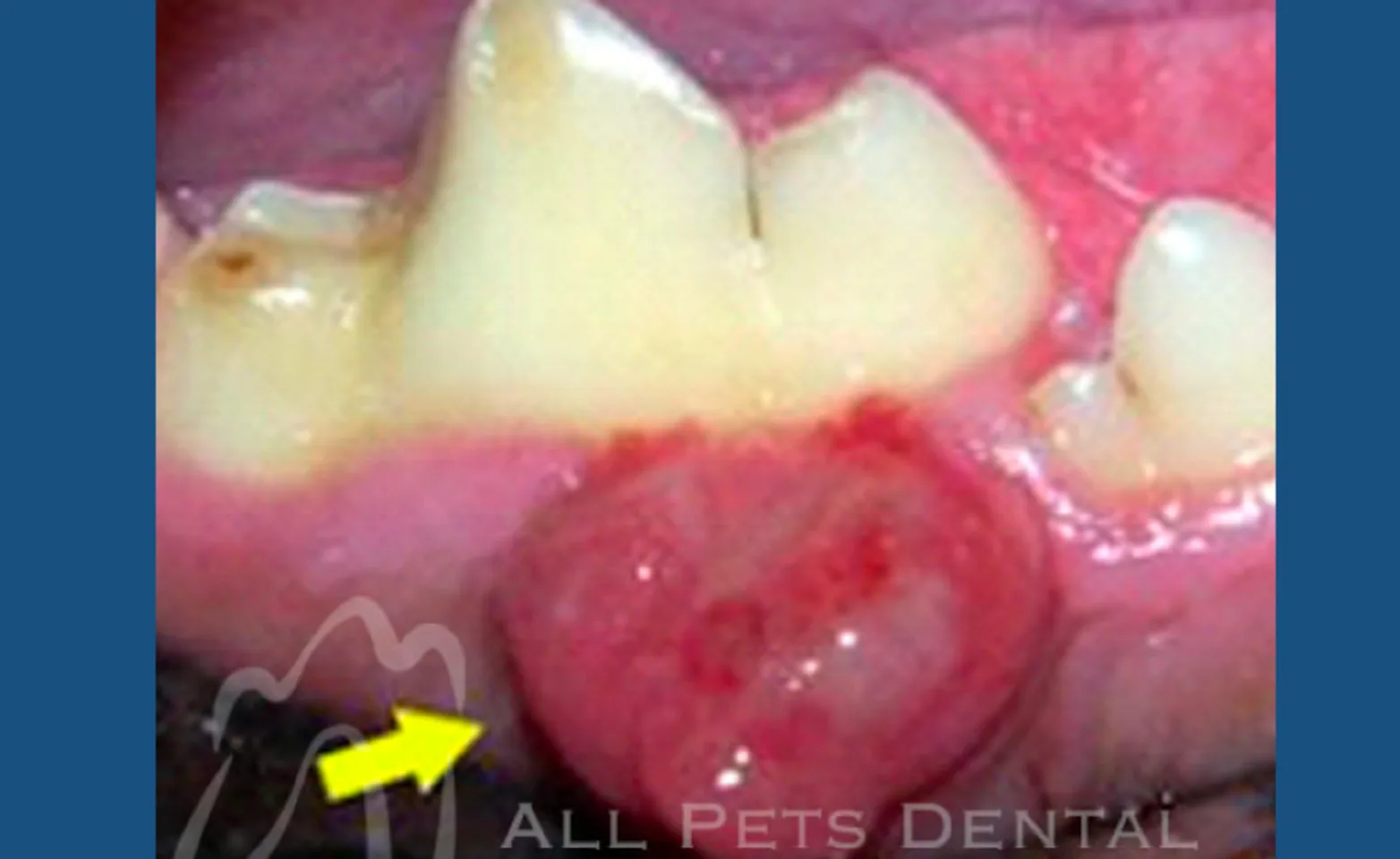
Acanthomatus Ameloblastoma
The acanthomatous ameloblastoma occurs commonly in dogs. This tumor is considered benign because it does not spread to distant locations however it can be locally invasive. Treatment of acanthomatus ameloblastoma is wide excision in all planes.
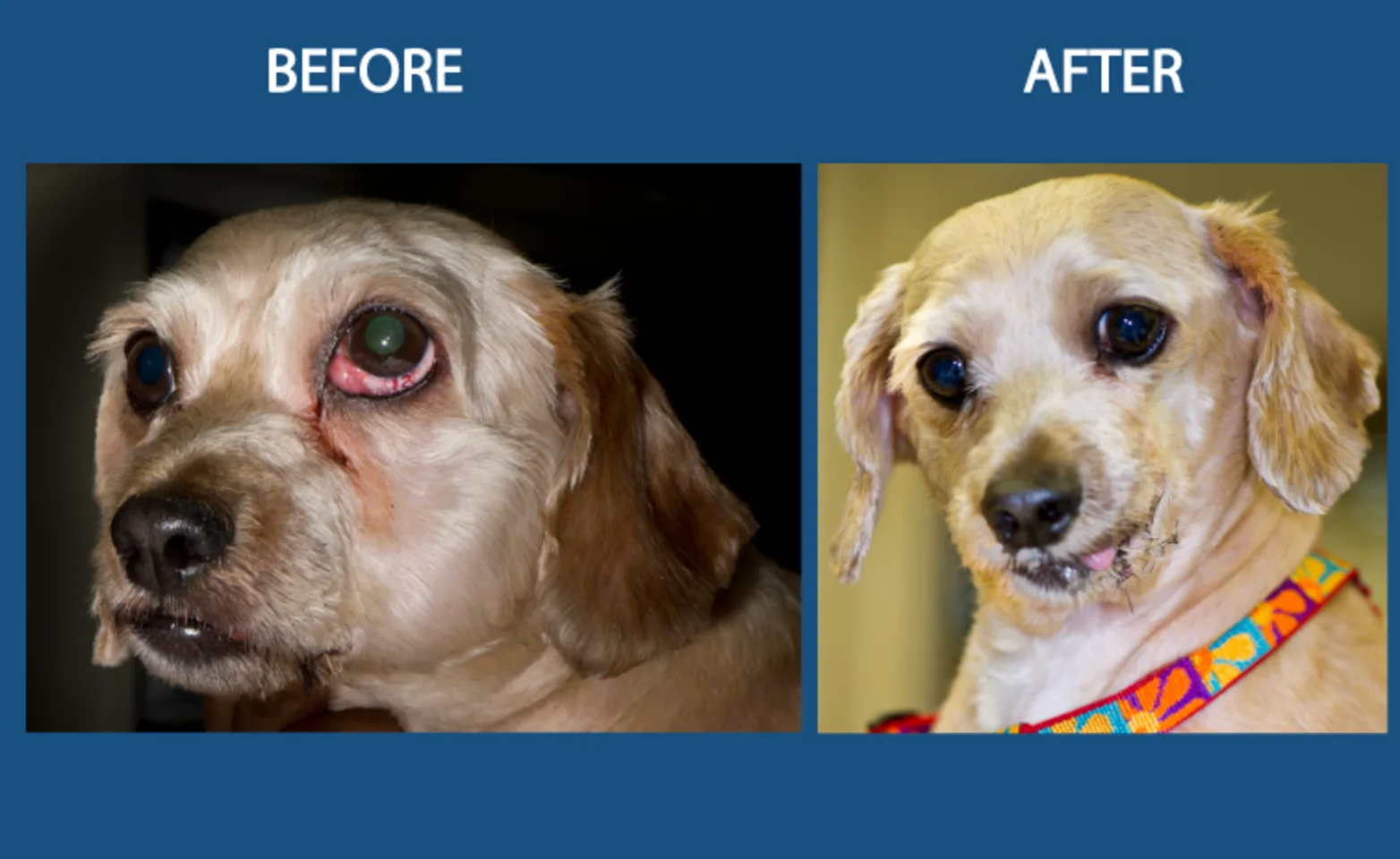
Tumor Surgery
Often dogs develop noticeable swellings on their faces. These can be due to tooth infections or tumors. Fortunately many swellings can be treated and dogs cured.
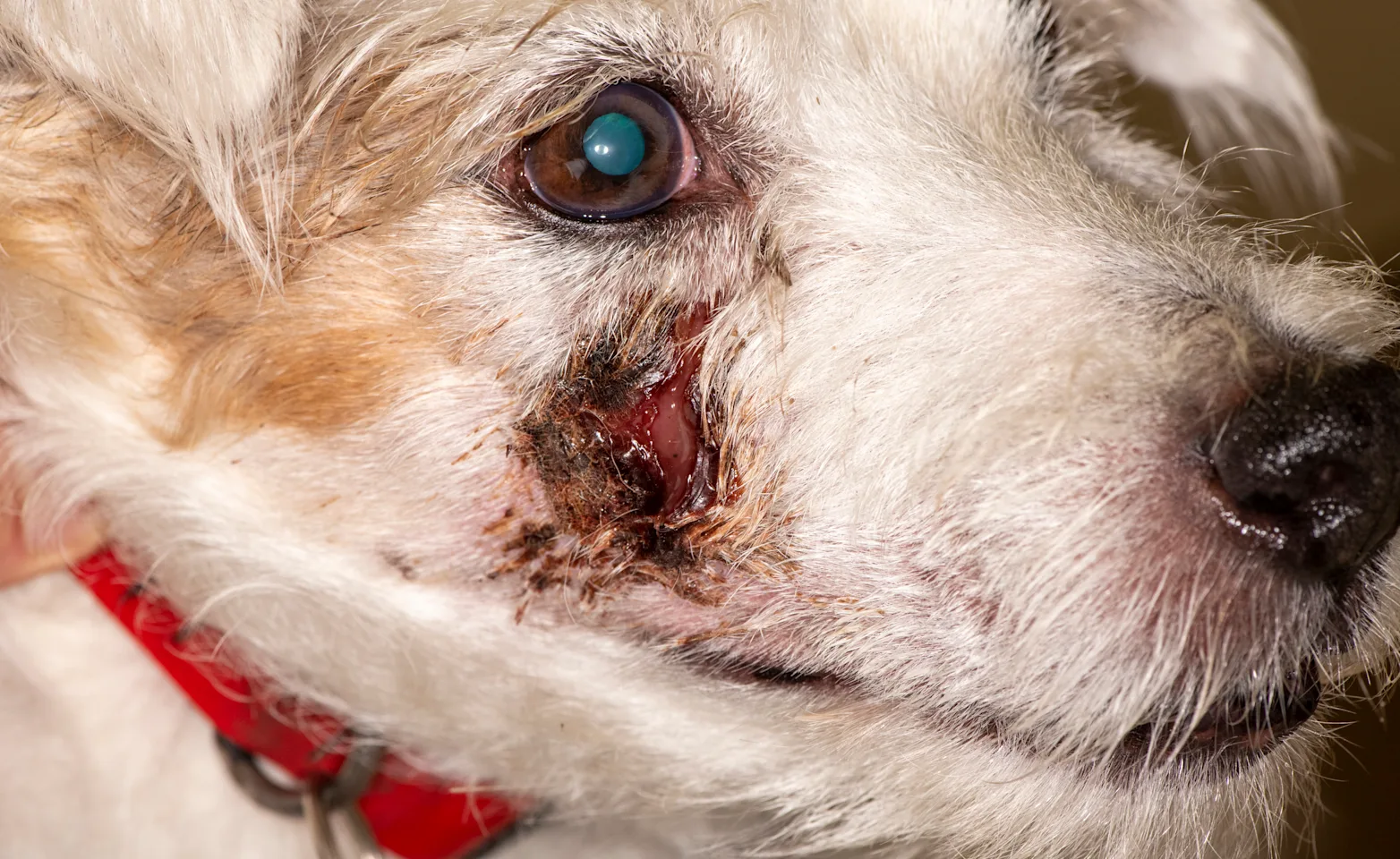

Facial Discharge
Before Treatment
Facial swelling and discharge due to infection caused from a broken tooth
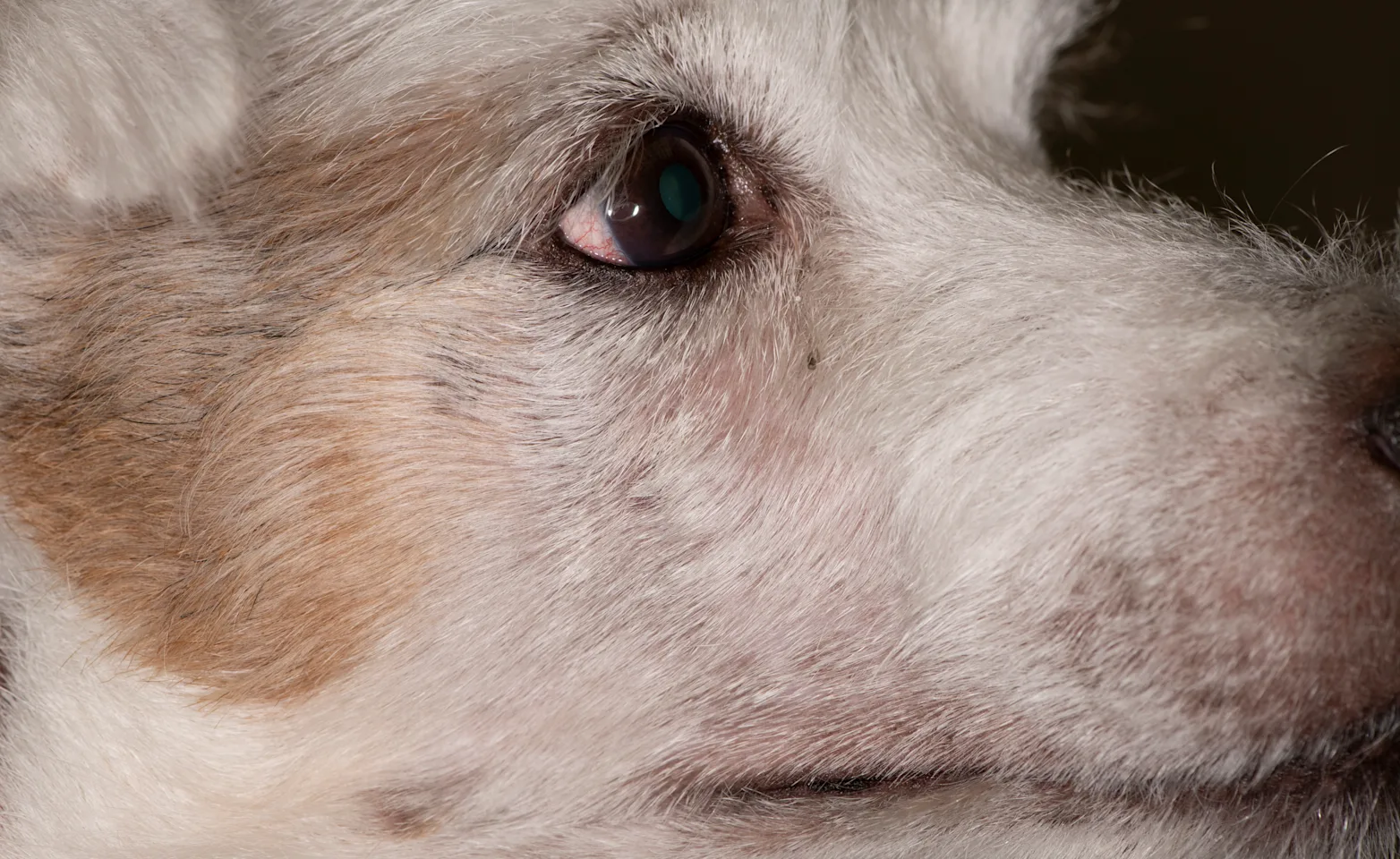

Facial Swelling
After Treatment
Swelling resolved after tooth extraction
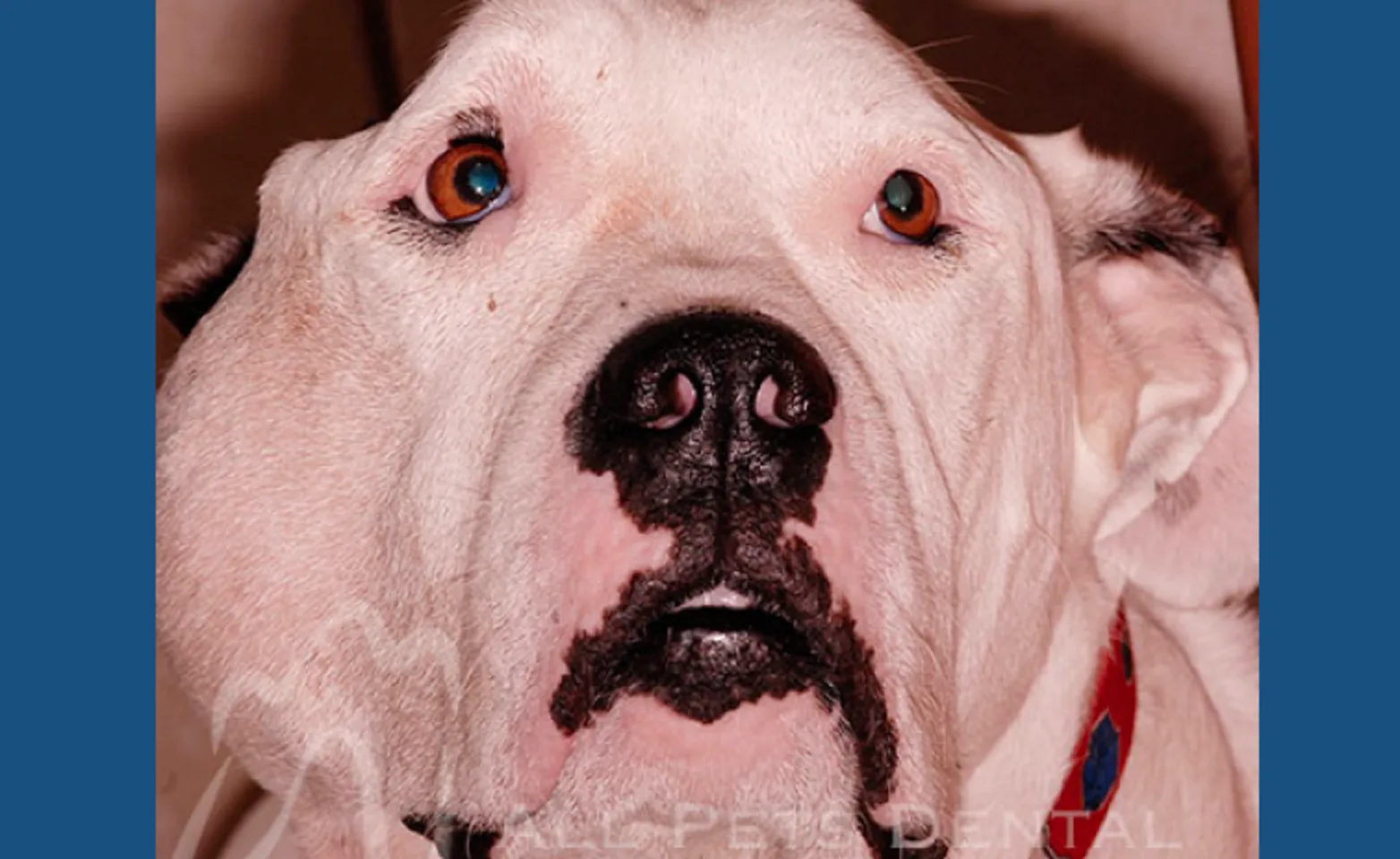

Fibrosarcoma
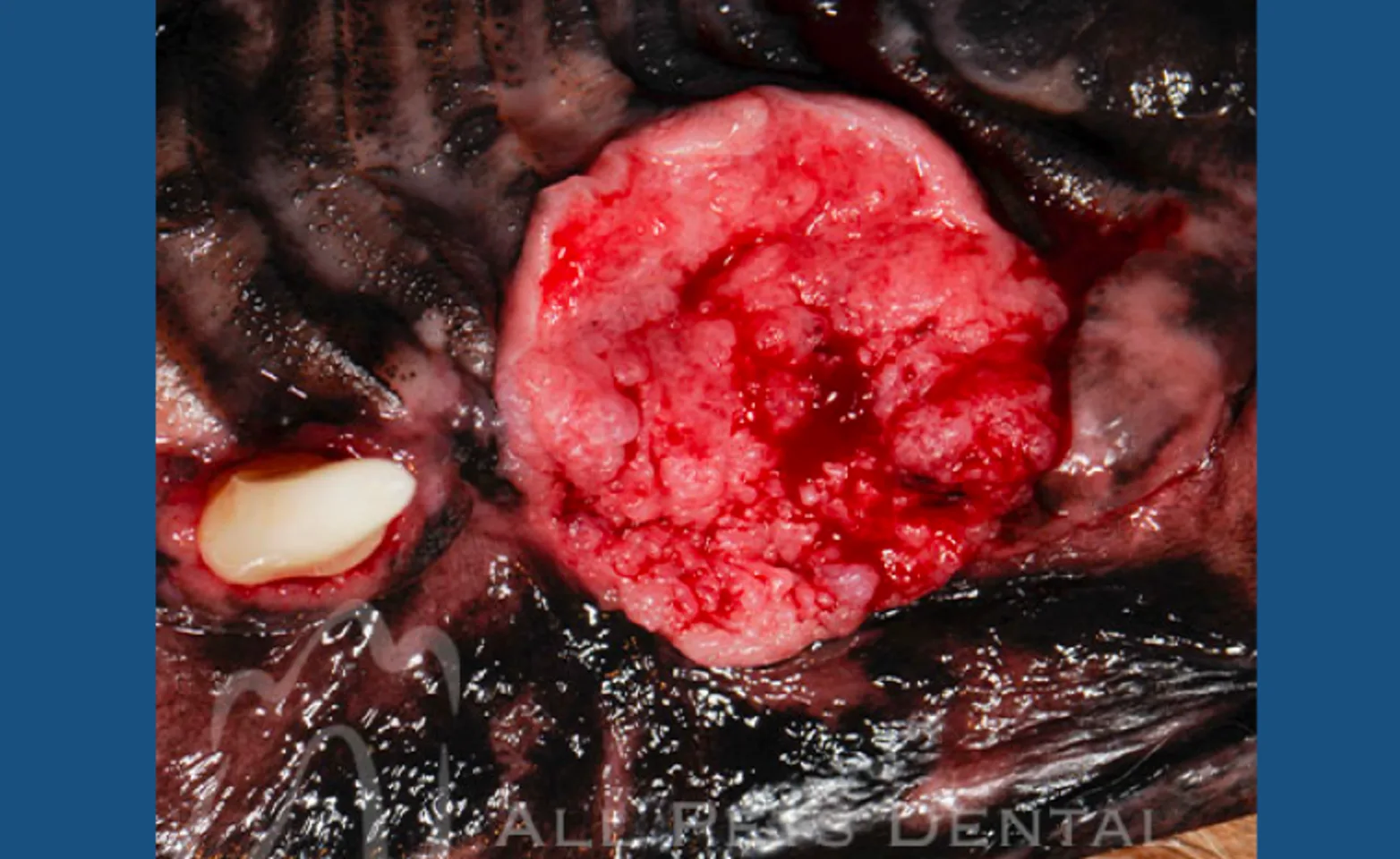
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The second most common malignant tumor in the dog. Treatment of choice is surgical removal with a guarded prognosis.
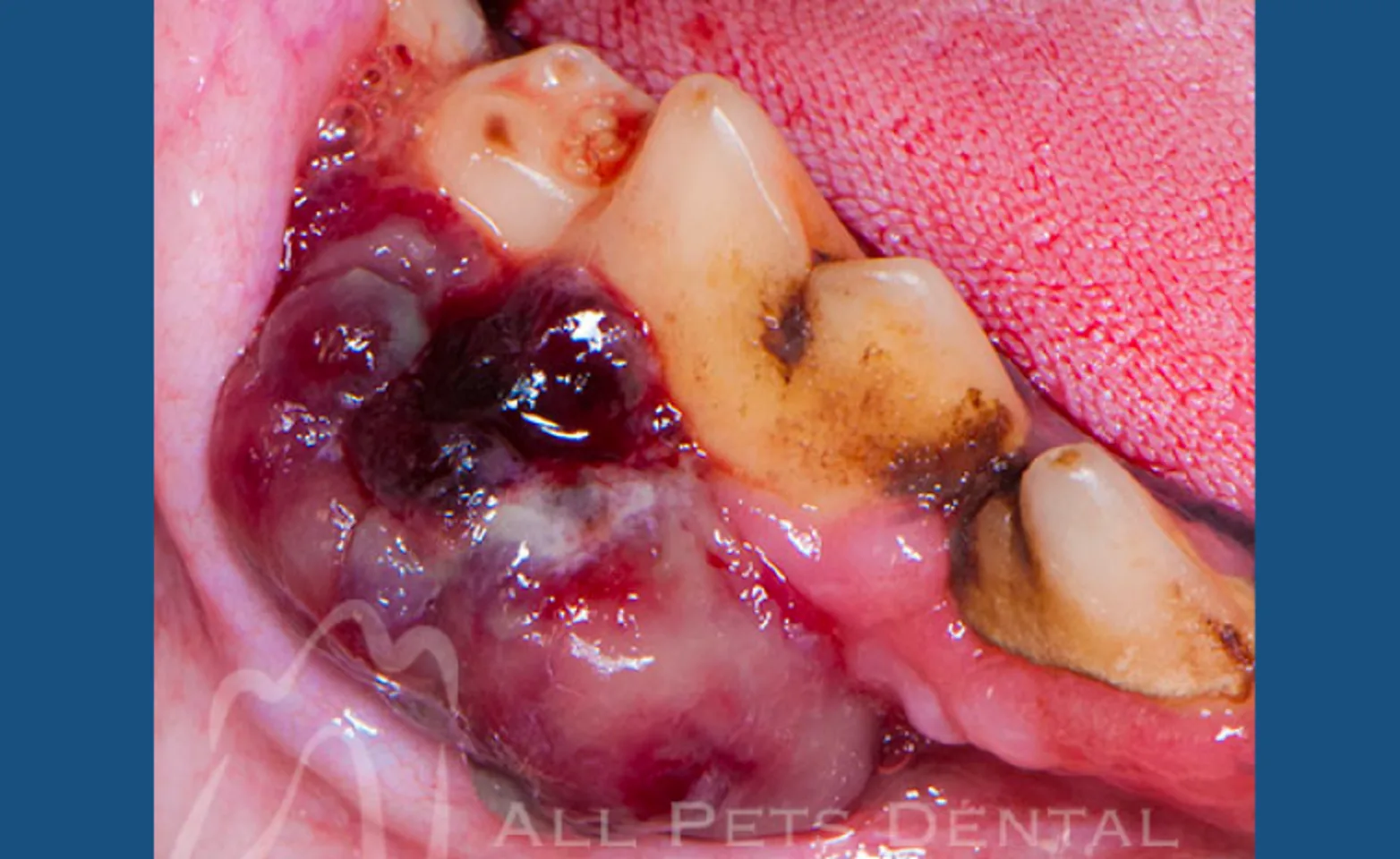
Malignant Melanoma
The most commonly diagnosed malignant oral tumor in the dog. Treatment options include surgical removal with wide margins, radiation therapy, and use of the canine melanoma vaccine.
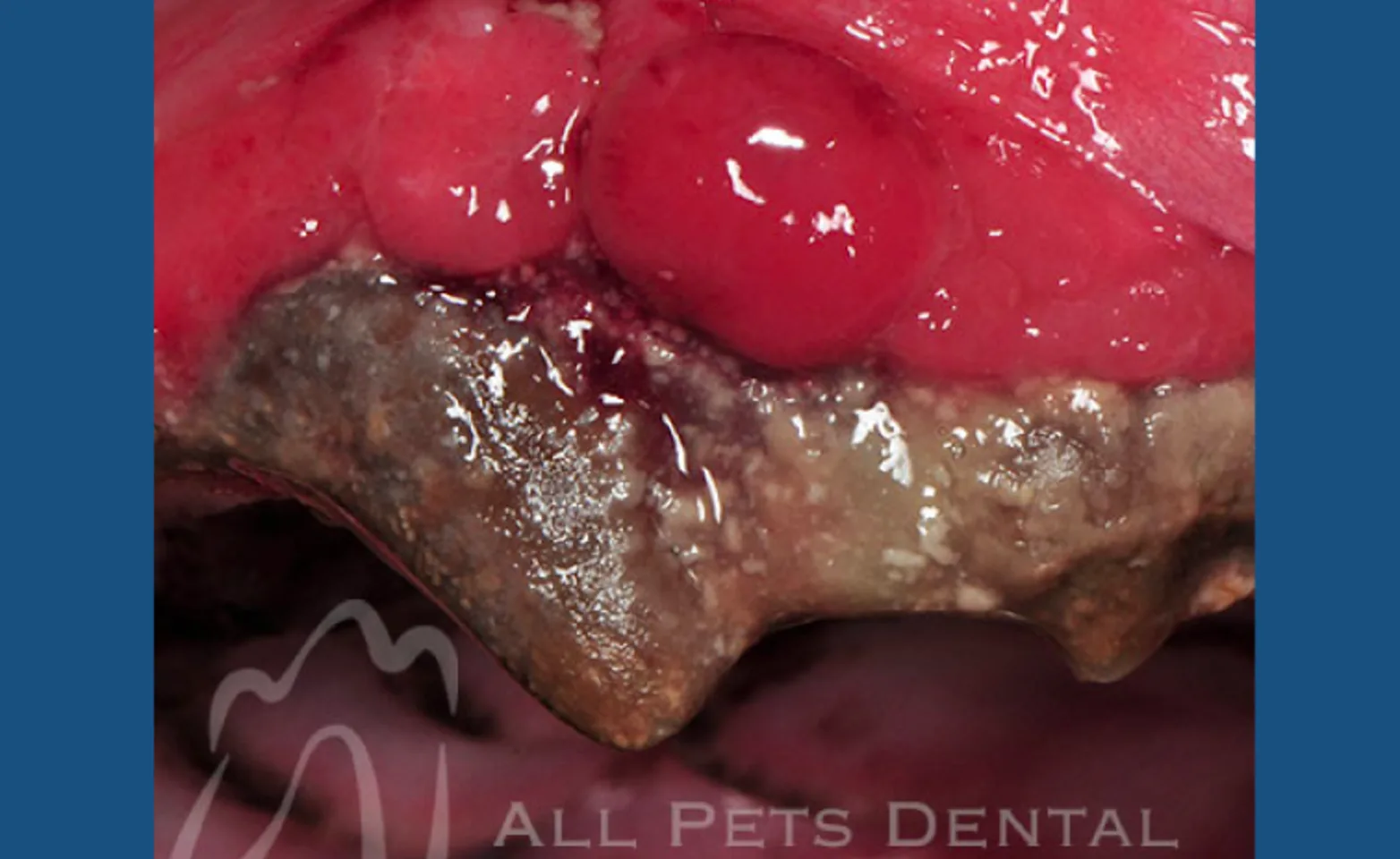
Plasmacytoma
Plasmacytoma is a malignant tumor if plasma cells. Treatment options include surgical removal with wide margins.
