Hometown Animal Hospital

Canine Development Problems
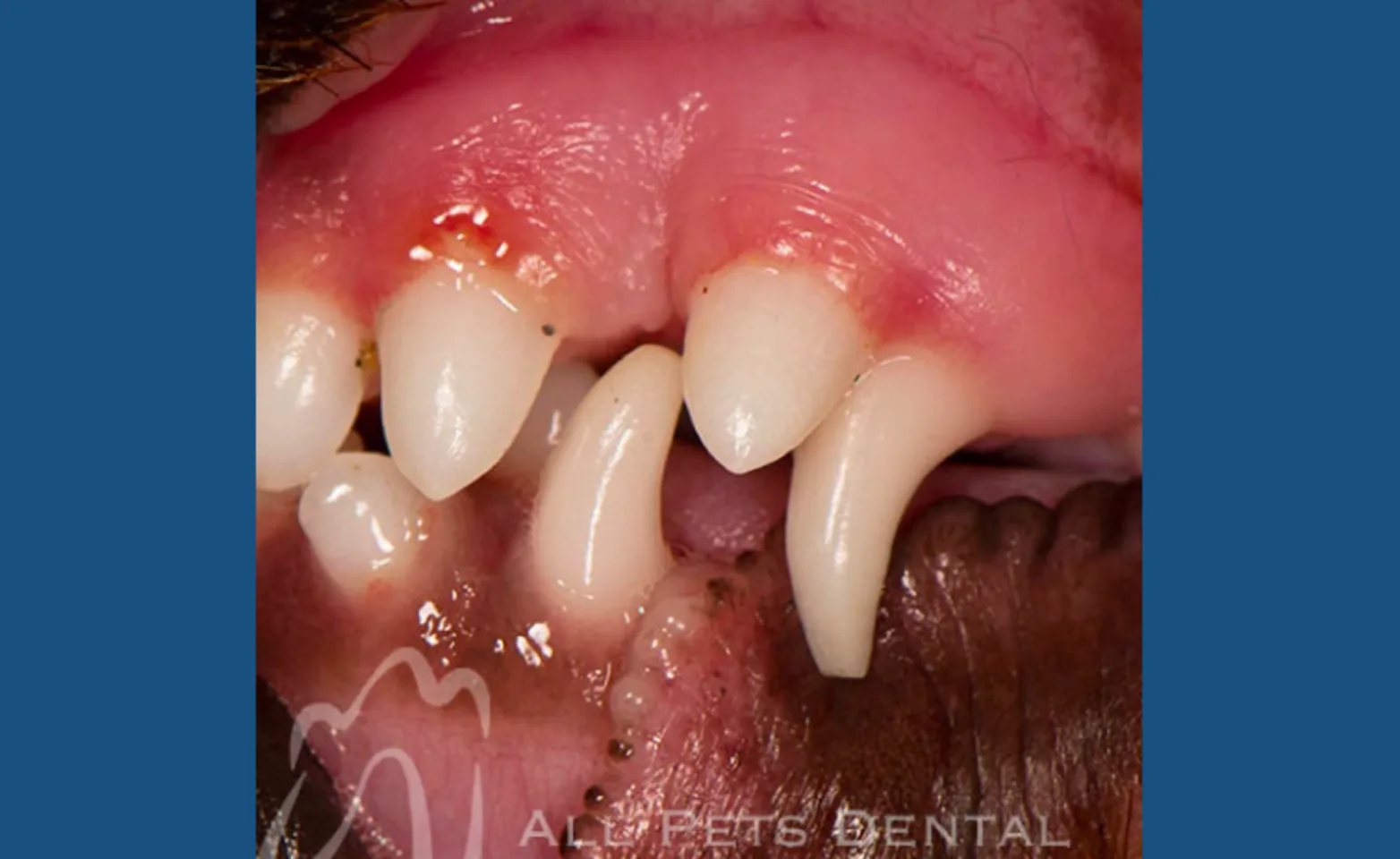
Retained Deciduous Teeth
Also referred as a persistent primary tooth, a retained deciduous tooth occurs when the adult tooth fails to push the baby tooth from its socket. Retained deciduous teeth should be extracted to prevent orthodontic and/or periodontal future problems.
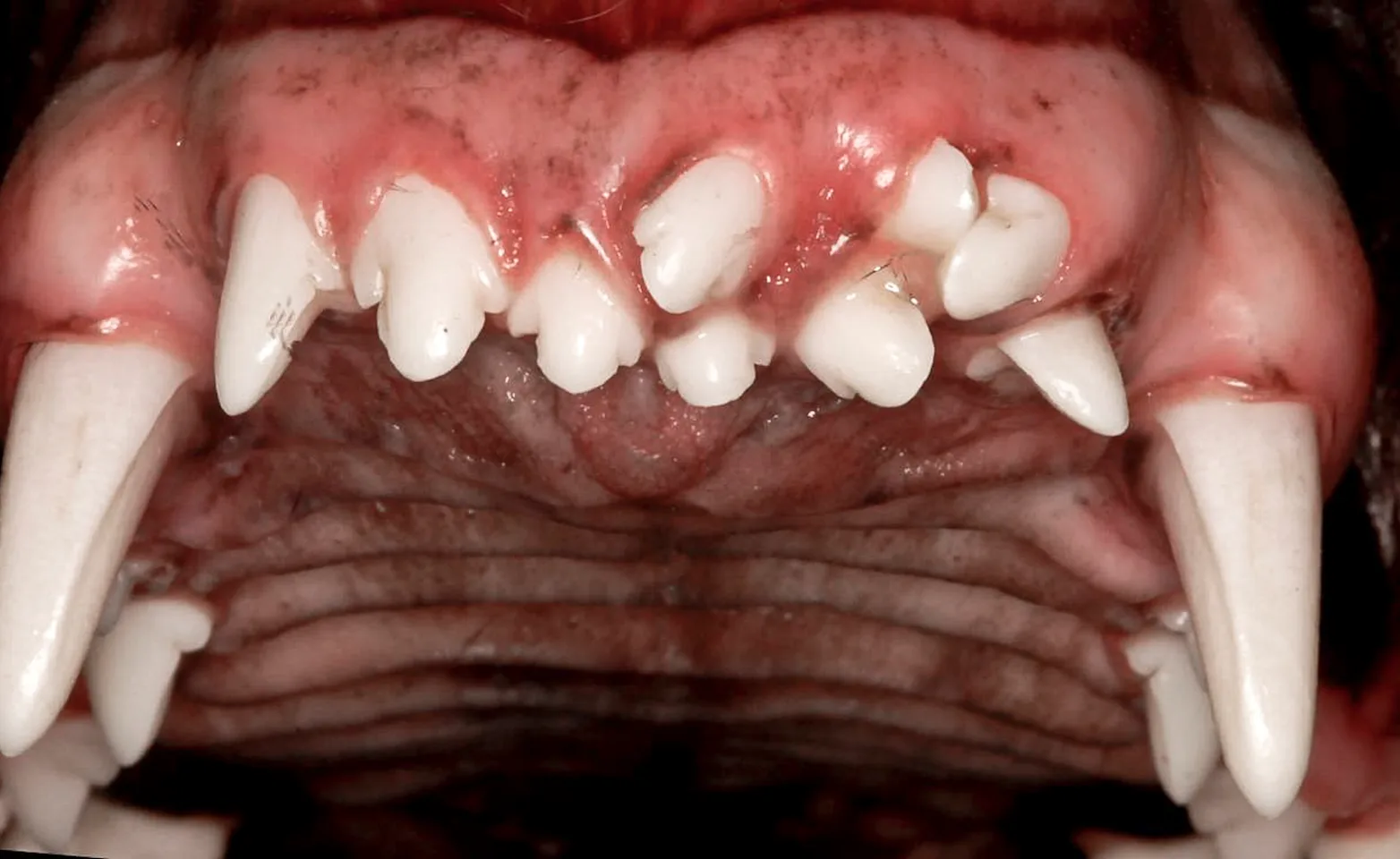
Supernumerary Teeth
Supernumerary teeth occur when one or more extra permanent teeth erupt in the oral cavity. Treatment of choice is to remove the extra tooth giving the normal teeth enough room.
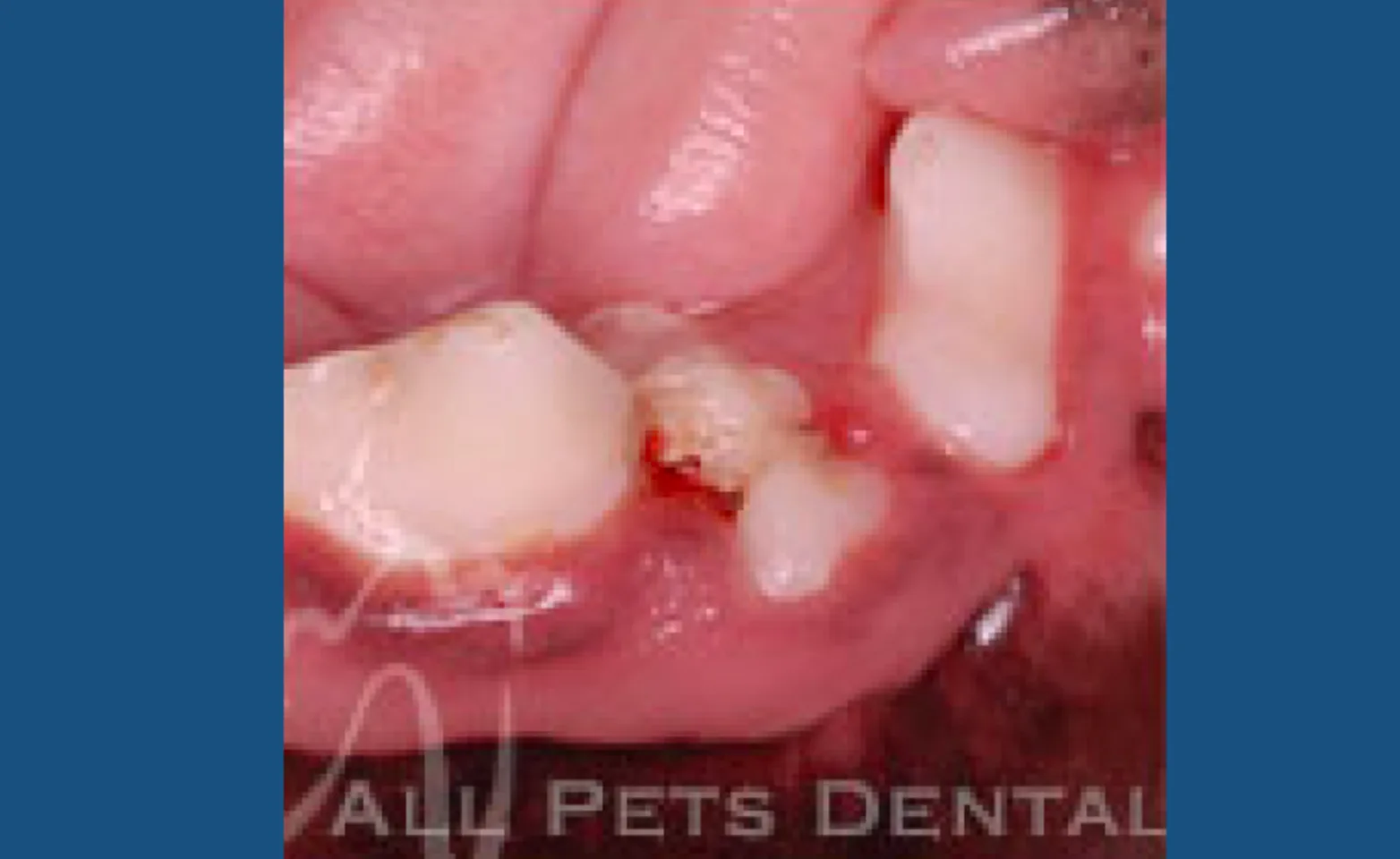
Rotated Teeth
Normally teeth should be orientated to follow a natural arch. Occasionally a rotated tooth is positioned perpendicular to the normal arch. Extraction of the abnormal tooth is indicated to help prevent periodontal disease.
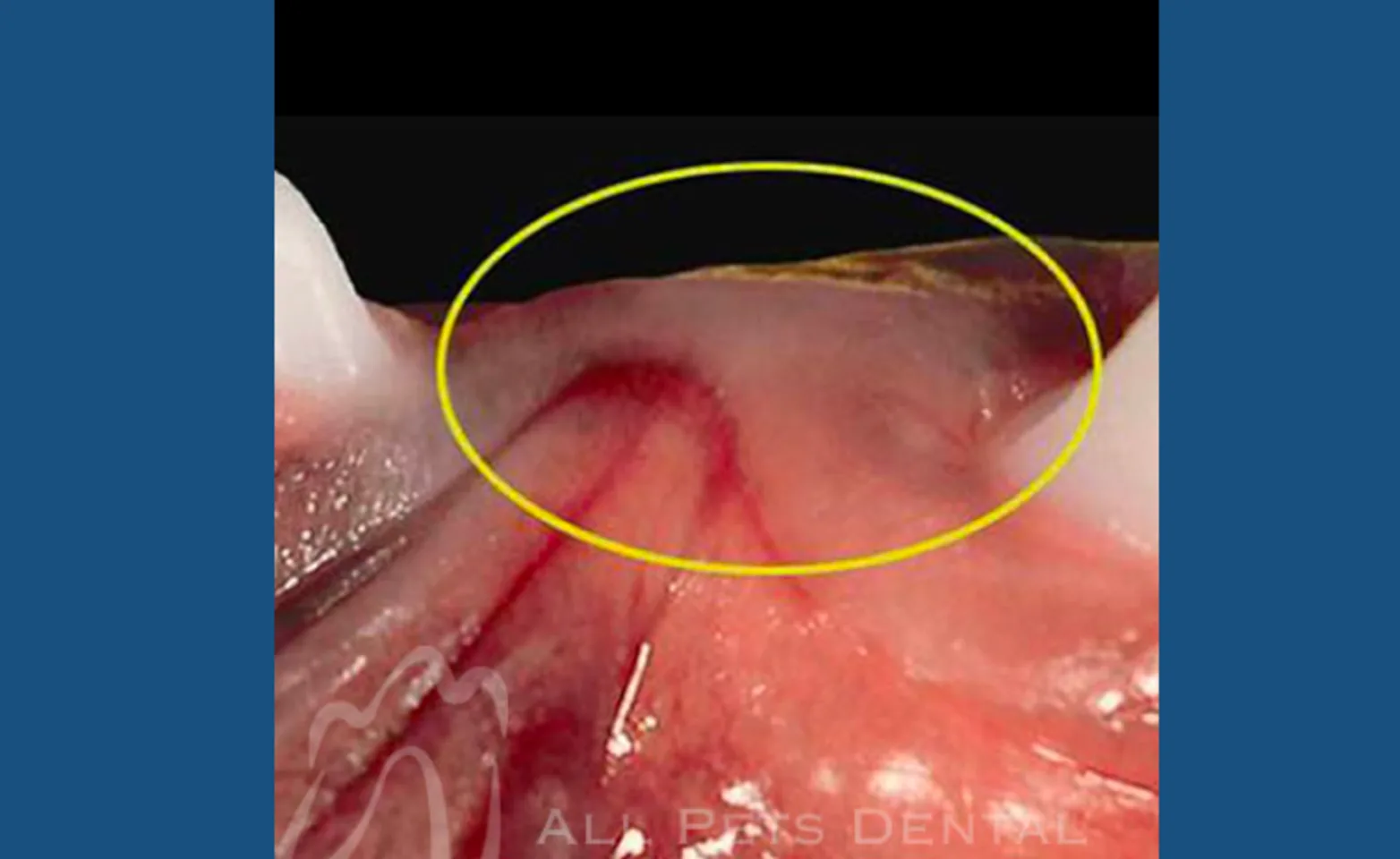
Missing Teeth
Occasionally there will be a visible area where a tooth should be but is not apparent. In some cases the crown has been traumatically removed leaving a root. In other cases the dog or cat was born without a tooth in the area. X-rays should be taken to evaluate the area beneath the gum line for fractured roots, impacted teeth, and cysts.
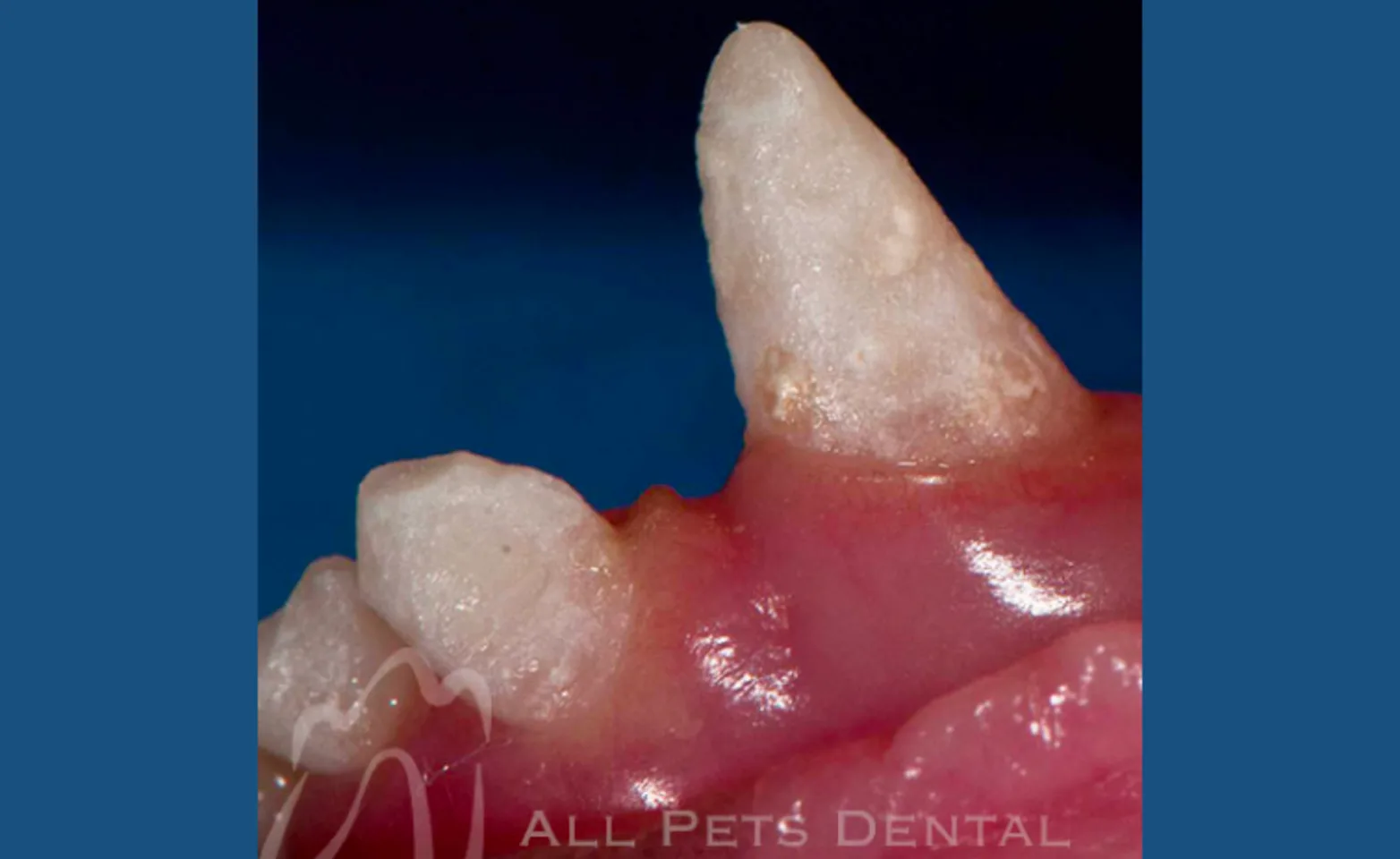
Enamel Hypomineralization
Enamel hypomineralization occurs when there is normal enamel matrix deposition with inadequate mineralization resulting in decreased enamel over all crown surfaces resulting in a dull appearance. Treatment entails placing a light cured dental sealant over the tooth crack.
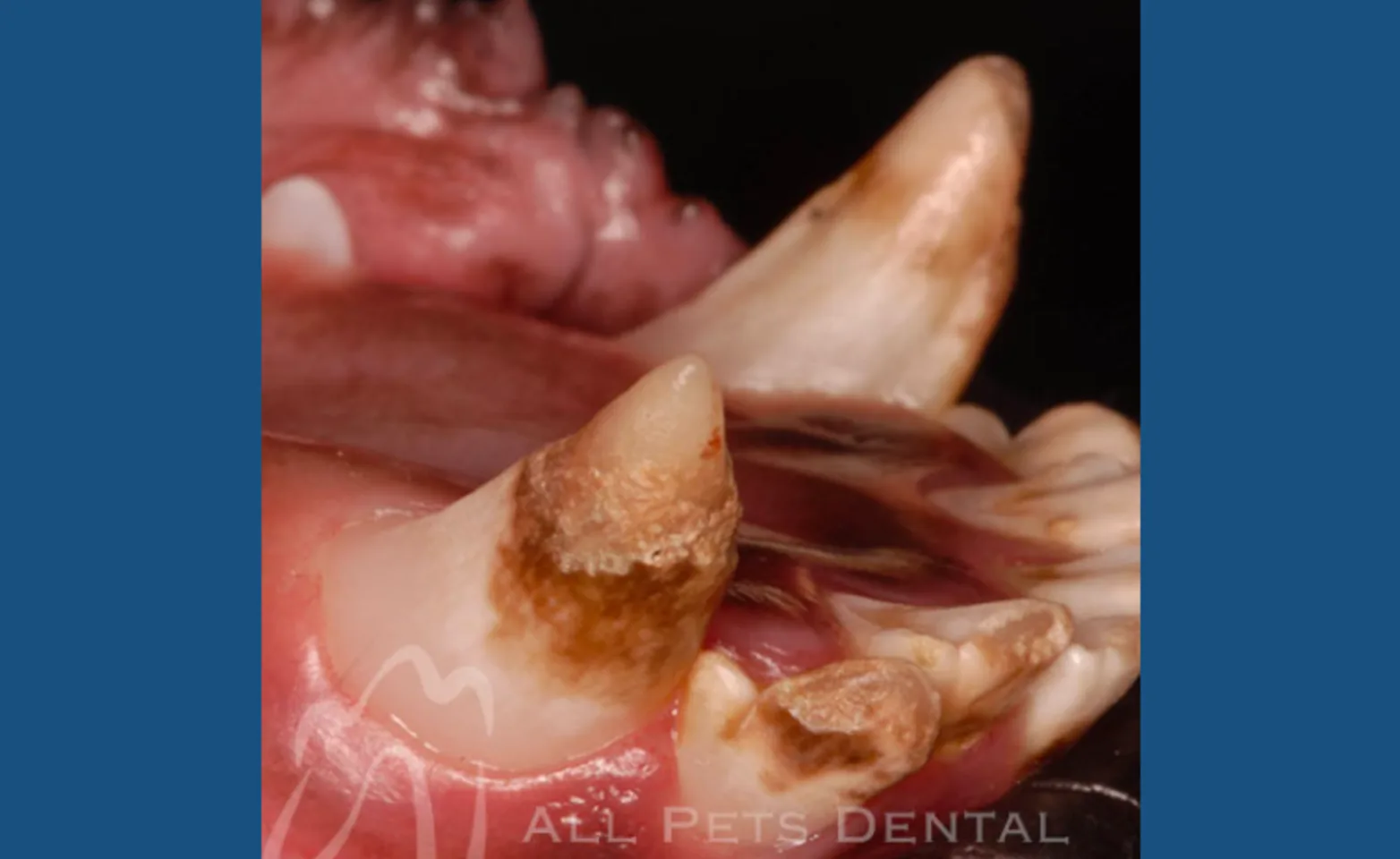
Enamel Hypoplasia
Localized enamel hypoplasia occurs when there is an inadequate deposition of enamel matrix resulting in clinically normal appearing areas of the crown as well as areas of missing enamel exposing underlying dentin. This condition exposes dentin which can be painful. Restoration of the tooth is recommended.
